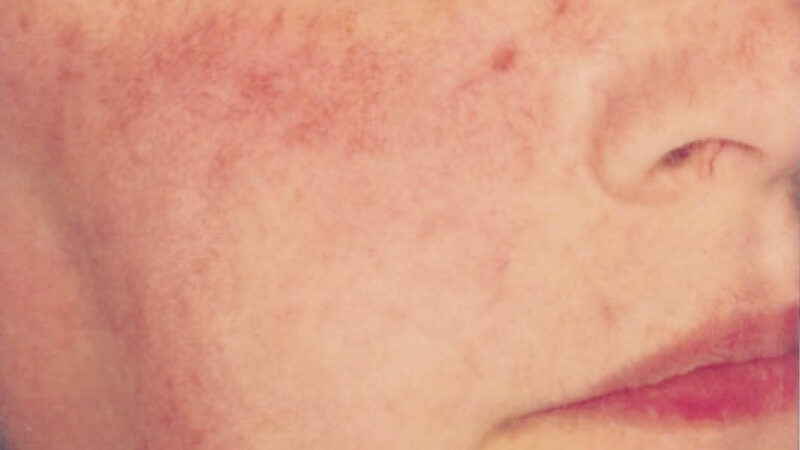
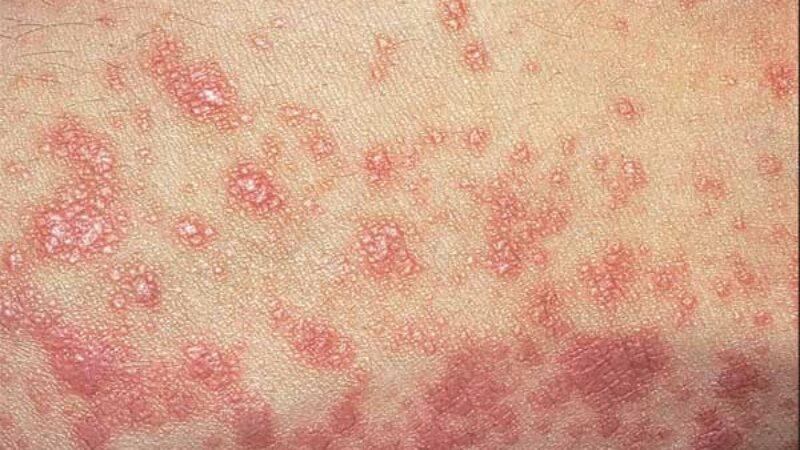
Solar urticaria is a rare skin condition that occurs upon exposure to ultraviolet radiation or ultraviolet light. It manifests as a case of urticaria or itchy hives often accompanied by redness. Hives occur in areas covered by thin clothing as well as uncovered areas. And, skin that is more frequently exposed to the sun (like the face) is typically unlikely to develop hives compared to skin that has less frequent sun exposure. The symptoms of solar urticaria may be confused with a sunburn or polymorphous light eruption (PMLE); it tends to go away quickly (less than a day in most cases) once sun exposure has stopped.
Solar urticaria is a rare skin condition that occurs upon exposure to ultraviolet radiation or ultraviolet light. It manifests as a case of urticaria or itchy hives often accompanied by redness. Hives occur in areas covered by thin clothing as well as uncovered areas. And, skin that is more frequently exposed to the sun (like the face) is typically unlikely to develop hives compared to skin that has less frequent sun exposure. The symptoms of solar urticaria may be confused with a sunburn or polymorphous light eruption (PMLE); it tends to go away quickly (less than a day in most cases) once sun exposure has stopped.
It’s still not known what agent causes the reaction responsible for solar urticaria although it seems that individuals who develop it may make allergic antibodies against proteins found in their own skin.
Solar urticaria is treated with the use of antihistamines along with topical steroid creams such as hydrocortisone. More severe symptoms may require treatment with oral steroids. Repeated exposures to sunlight may be used to desensitize skin so that hives will not occur with future exposures to sunlight.