When it comes to the sun and the damage it can wreak upon skin, it’s the sun’s UV rays that we’re concerned about most. In this post I discuss the different types of UV rays and the impact they have on your skin. Plus, I”ll look at ways to protect yourself.
The sun emits all kinds of electromagnetic radiation, with 99% of it being rays in the form of visible light, ultraviolet (UV) rays and infrared rays. Visible light helps us see, infrared rays help keep us warm and UV rays carry energy. When it comes to skin, we are concerned with UV rays because the energy contained in them can change the chemical structure of molecules, causing cell damage and possibly deformities by actually mutating its genetic code.
About UV Rays
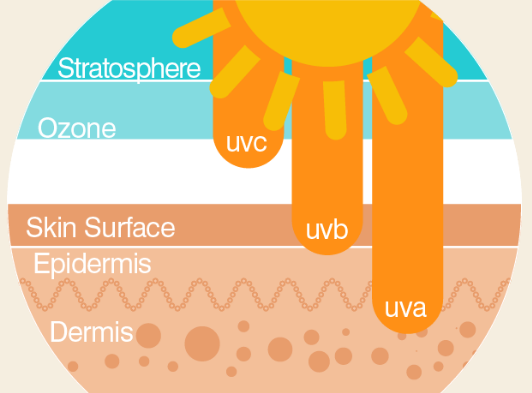
There are 3 main types of UV rays – UVA, UVB and UVC. UVA rays have the longest wavelengths, followed by UVB, and UVC rays which have the shortest wavelengths. UV-C is the most energetic and most harmful; UV-A is least energetic and least harmful. Fortunately, UVC rays break apart when they reach the earth’s protective ozone layer so the sun’s UVC rays never reach us. UVC rays can be man-made (as in welding) and they are just as dangerous as the natural ones.
UVA and UVB rays reach the earth’s surface and both can be detrimental to our health. Most of the UV rays you come in contact with are UVA with a small amount of UVB:
- UVB rays have a short wavelength and reach the outer layer of your skin (the epidermis). They are responsible for Burning skin.
- UVA rays have a longer wavelength and can penetrate the middle layer of your skin (the dermis). They are responsible for Aging skin.
Both types of rays can contribute to skin cancer with prolonged exposure.
Some medicines, including antibiotics, birth control pills, and topical benzoyl peroxide products, along with some cosmetics, may increase skin and eye sensitivity to UV rays. Tanning booths, mercury vapor lighting (often found in stadiums and school gyms), some halogen, fluorescent, and incandescent lights and some types of lasers are also sources of UV radiation.
What About Vitamin D?
 Although you need exposure to UVB radiation to help produce vitamin D, the amount of exposure necessary depends on several factors including:
Although you need exposure to UVB radiation to help produce vitamin D, the amount of exposure necessary depends on several factors including:
- Your Skin Colour (Darker skin requires longer exposure to UVB rays to produce Vitamin D)
- Sunscreen Use and Clothing
- Where You Live (latitude and altitude). UV rays are strongest in areas close to the equator and lower in areas further from the equator because the sun is farther away. Higher altitudes have greater UV exposure because there is less atmosphere to absorb UV rays. Snow, sand, pavement, and water can increase UV exposure due to their reflective properties.
How To Be Sun Safe
The best way to protect your skin against UV ray damage is to reduce the amount of time you spend in the sun, particularly between the hours of 10 am and 4 pm, when the sun is at its highest in the sky. While this isn’t always possible, there are some additional ways you can protect yourself:
- Stay out of the sun during the peak sun hours of 10am and 4pm, especially during the summer.
- Stay indoors or seek shade.
- Wear hats, protective clothing and sunscreen to cover yourself. Protect your eyes and the skin around your eyes with a large pair of sunglasses.
- Wear Sunscreen. This is important, even in cloudy weather. UVA rays can penetrate through clouds (and windows) causing long-term damage. Get into the habit of using sunscreen every day, year round.
UV rays surround us daily and are one of the biggest contributors to skin damage. It is possible to protect yourself.