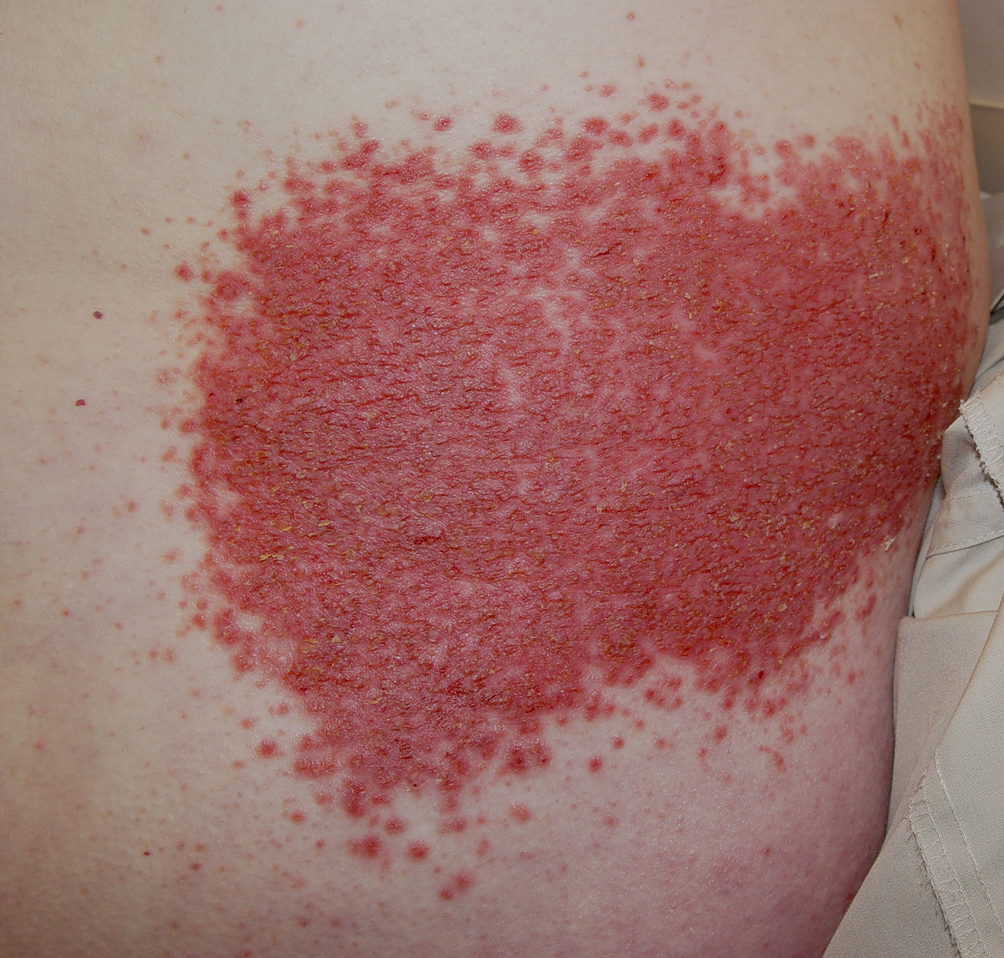
Keratosis follicularis (also known as Darier’s disease or Darier-White disease) is a non-contagious skin ailment characterized by crusty, scaly skin in oily areas of the body which are exposed to light. Scientists believe it is caused by an abnormality in one of the components of skin. Symptoms include fissures (skin cracks), fingernail ridges, and/or an odorous rash. UV rays (UVB in particular), stress, friction, hormones, heat and humidity can aggravate symptoms. The disease affects both men and women, and often begins in late adolescence, with symptoms appearing in adulthood. It is common for those suffering from keratosis folicularis to be particularly short in stature and/or to suffer from depression or mood disorders, suggesting a genetic link with these conditions.
Treatment
If you are diagnosed with keratosis follicularis, it’s important to work with your doctor to minimize the symptoms associated with the condition.
1. Avoid irritation of the skin by using gentle cleansers and moisturizers. Keeping cool is also important.
2. A tretinoin (Vitamin A) cream or a topical corticosteroid may help to keep the irritation under control. Other drugs which may help include etretinate and acitretin, topical 5FU , Cyclosporine, and oral contraceptives (in the case of hormonally related flare-ups).
3. Well formulated UVA/UVB blocking sunscreens (think Anthelios sunscreens or Ombrelle sunscreens) as well as topical vitamin C (apothekari Antioxidant C+E Serum, or La Roche Posay Redermic) are both effective in preventing symptoms.
4. A diet rich in essential fatty acids helps to keep symptoms in check. Look for healthy fats in salmon or fish oil supplements.
5. Persistent rashes may benefit from laser treatment.
6. In extreme cases, surgery may help to eradicate the symptoms.